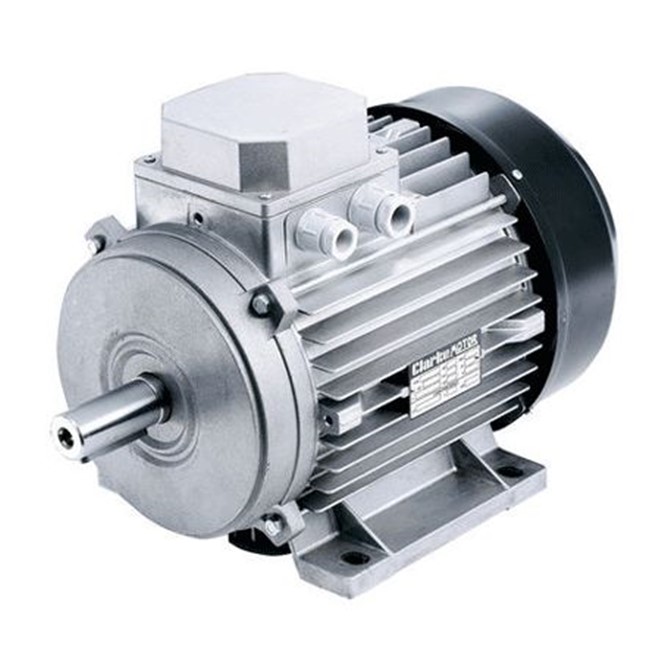
Gear reduction motor refers to the combination of gear reduction box and motor. This kind of composition is usually also called a gearbox motor or a geared motor, and is usually supplied as a complete set after being integrated and assembled by a professional gear reducer manufacturer.
Geared motors are widely used and are indispensable power transmission equipment for automated machinery and equipment, especially in packaging machinery, printing machinery, corrugated machinery, color box machinery, conveying machinery, food machinery, three-dimensional parking lot equipment, automatic storage, and three-dimensional warehouses. , Chemical, textile, dyeing and finishing equipment. Miniature geared motors are also widely used in electronic locks, optical equipment, precision instruments, financial equipment and other fields.
working principle:
Gear reducer motors generally use electric motors, internal combustion engines or other high-speed running power to drive the large gears to achieve a certain deceleration through the pinion on the input shaft of the gear reducer (or reduction box), and then adopt a multi-stage structure. Greatly reduce the speed to increase the output torque of the geared motor. Its core function of "increasing and decelerating" is to use all levels of gear transmission to achieve the purpose of speed reduction, and the reducer is composed of various levels of gear pairs.

Overview:
1. The geared motor is manufactured in accordance with international technical requirements and has a high technological content.
2. Compact structure, reliable and durable, high overload capacity and high power.
3. Low energy consumption, superior performance, and the reducer efficiency is as high as 95%.
4. Low vibration, low noise, high energy saving, high-quality section steel materials, rigid cast iron box body, high-end gear reducer motor adopts special aluminum alloy die-cast box body, and the gear surface undergoes high frequency heat treatment.
5. After precision processing to ensure positioning accuracy, the gear reducer motor of the reducer gear transmission assembly can be equipped with various mainstream motors in the market, forming a new product feature of electromechanical integration and modular structure, which fully guarantees the quality of product use.
6. The product adopts serialized and modular design ideas, and has a wide range of adaptability. It can be combined with various motors, installation positions and structural schemes, and the gear reducer can choose any speed and various structural forms according to actual needs.
Features
Features of gear reducer:
1. The gear reducer motor is manufactured according to the national professional standard ZBJ19004 production technical requirements;
2. It saves space, is reliable and durable, with high overload capacity, and the power can reach more than 95KW;
3. Low energy consumption, superior performance, and the reducer efficiency is as high as 95% or more;
4. Low vibration, low noise, high energy saving, high-quality steel material, rigid cast iron box body, high-frequency heat treatment on the surface of the gear;
5. After precision machining, the positioning accuracy is ensured. The gear reduction motor that constitutes the gear transmission assembly is equipped with various motors, forming an electromechanical integration, which fully guarantees the quality characteristics of the product;
6. The product adopts a serialized and modular design concept, and has a wide range of adaptability. This series of products has an extremely large number of motor combination installations, installation positions and structural schemes. Any speed and various structural forms can be selected according to actual needs.

The reducer includes a gearbox, which is divided into high-power reducer and low-power reducer according to power; high-power reducer is used in ships, locomotives, transportation, docks, lifting, construction, mining, steel, non-ferrous metals, heavy industry manufacturing, etc. Industry; low-power reducers are used in smart homes, household appliances, communication antennas, electronic products, aerial photography equipment, security fields, car drives, driving systems, robotics equipment, logistics and storage equipment, smart homes, smart cities, artificial intelligence, etc. field.
An electric motor, also known as a motor or an electric motor, is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, and can then use the mechanical energy to generate kinetic energy to drive other devices. There are many types of motors, but they can be roughly divided into AC motors and DC motors for different occasions.
The advantage of a DC motor is that it is relatively simple in speed control. It only needs to control the voltage to control the speed. However, this type of motor is not suitable for operation in high temperature, flammable and other environments, and because the motor needs to use carbon brushes as a Commutator components (brush motors), so it is necessary to regularly clean up the dirt generated by carbon brush friction. A brushless motor is called a brushless motor. Compared with a brush, a brushless motor is less power-saving and quieter because of the less friction between the carbon brush and the shaft. The production is more difficult and the price is higher. AC motors can be operated in high temperature, flammable and other environments, and do not need to clean the carbon brush dirt regularly, but it is more difficult to control the speed, because controlling the speed of the AC motor needs to control the frequency of the AC (or use induction The motor uses the method of increasing the internal resistance to reduce the motor speed at the same AC frequency), and controlling its voltage will only affect the torque of the motor. Generally, the voltage of civil motors is 110V and 220V. In industrial applications, there are also 380V or 440V.

working principle
The principle of rotation of the motor is based on John Ambrose Fleming's left-hand rule. When a wire is placed in a magnetic field, if the wire is energized, the wire will cut the magnetic field line and move the wire. The electric current enters the coil to generate a magnetic field, and the magnetic effect of the electric current is used to make the electromagnet continuously rotate in the fixed magnet, which can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It interacts with a permanent magnet or a magnetic field generated by another set of coils to generate power. The principle of a DC motor is that the stator does not move, and the rotor moves in the direction of the force generated by the interaction. The AC motor is the stator winding coil is energized to generate a rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field attracts the rotor to rotate together. The basic structure of a DC motor includes "armature", "field magnet", "snumeric ring", and "brush".
Armature: A soft iron core that can rotate around an axis is wound with multiple coils. Field magnet: A powerful permanent magnet or electromagnet that generates a magnetic field. Slip ring: The coil is connected to two semi-circular slip rings at about both ends, which can be used to change the direction of the current as the coil rotates. Every half a turn (180 degrees), the direction of current on the coil changes. Brush: Usually made of carbon, the collector ring is in contact with the brush in a fixed position to connect to the power source.
Basic structure
There are many types of electric motors. In terms of basic structure, its composition is mainly composed of a stator (Stator) and a rotor (Rotor).
The stator is stationary in the space, while the rotor can rotate around the shaft and is supported by bearings.
There will be a certain air gap between the stator and the rotor to ensure that the rotor can rotate freely.
The stator and the rotor are wound with coils, and current is applied to generate a magnetic field, which becomes an electromagnet. One of the stator and the rotor can also be a permanent magnet.

The following are all called motors
Classified by power supply:
name
characteristic
DC motor
Use permanent magnets or electromagnets, brushes, commutators and other components. The brushes and commutators continuously supply the external DC power supply to the coil of the rotor, and change the direction of the current in time, so that the rotor can follow the same direction Continue to rotate.
AC motor
The alternating current is passed through the stator coil of the motor, and the surrounding magnetic field is designed to push the rotor at different times and different positions to make it continue to run
*Pulse motor
The power source is processed by a digital IC chip and turned into a pulse current to control the motor. A stepping motor is a kind of pulse motor.
Classified by structure (both DC and AC power supplies):
name
characteristic
Synchronous motor
It is characterized by constant speed and no need for speed regulation, low starting torque, and when the motor reaches the running speed, the speed is stable and the efficiency is high.
Asynchronous motor
Induction motor
It is characterized by simple and durable structure, and can use resistors or capacitors to adjust the speed and forward and reverse rotation. Typical applications are fans, compressors, and air conditioners.
*Reversible motor
Basically the same structure and characteristics as the induction motor, it is characterized by a simple brake mechanism (friction brake) built into the tail of the motor. Its purpose is to achieve instant reversible characteristics by adding frictional load and reduce the effect of the induction motor. The amount of over-rotation generated by the force.
Stepping motor
It is characterized by a kind of pulse motor, a motor that rotates gradually at a certain angle. Because of the open-loop control method, it does not need a feedback device for position detection and speed detection to achieve precise position and speed control, and Good stability.
Servo motor
It is characterized by precise and stable speed control, fast acceleration and deceleration response, rapid action (fast reverse, rapid acceleration), small size and light weight, high output power (ie high power density), high efficiency, etc., and is widely used in position and speed control superior.
Linear motor
It has a long-stroke drive and can exhibit high-precision positioning capabilities.
other
Rotary Converter, Rotating Amplifier, etc.
Typical induction motors are widely used
There are many electric uses, ranging from heavy industries to small toys. Different types of electric motors are selected in different environments. Here are some examples: wind-making equipment, such as electric fans, electric toy cars, boats and other elevators, elevators powered by electricity, such as underground railways, tram factories and hypermarkets Electric automatic doors, electric rolling shutters, and people's livelihood supplies on transport belt buses
Optical drive, printer, washing machine, water pump, disk drive, electric razor, tape recorder, video recorder, CD turntable, industrial and commercial use
Fast elevator working machine (such as: machine tool) textile machine mixer

The principle of a motor and a generator are basically the same, and the directions of energy conversion are different. The generator converts mechanical energy and kinetic energy into electrical energy through a load (such as water power, wind power). If there is no load, the generator will not have current flowing out. The cooperation of electric motors, power electronics, and micro-controllers has formed a new discipline called motor control. Before using the motor, you need to know whether the power source is DC or AC. If it is AC, you also need to know whether it is three-phase or single-phase. Connecting the wrong power supply will cause unnecessary losses and dangers. After the motor is rotated, if the load is not connected or the load is light so that the motor speed is fast, the induced electromotive force is stronger. At this time, the voltage across the motor is the voltage provided by the power supply minus the induced voltage, so the current is weakened. If the load of the motor is heavy and the speed is slow, the relative induced electromotive force is smaller. Therefore, the power supply needs to provide a larger current (power) to output/work corresponding to the larger power required.
Output: Refers to the work that the motor can perform in a unit time, and is determined by the motor's operating speed and torque. Rated output: The motor can exert its best characteristics under rated voltage and rated frequency, and continuously produce various energy outputs, such as operating speed or torque. Usually, the rated output value is indicated on the motor nameplate. Asia usually uses watts (W) as the unit, while Europe and the United States use horsepower (HP).