What is the difference between dc motor and dc geared motor
Geared motor refers to the integrated body of reducer (gearbox) and motor (motor), which has the functions of deceleration, transmission, and torque enhancement. This kind of integrated body is usually called a gear motor or a gear motor. Different gearboxes and different drive motors have different functions, uses, and technical parameters. For example, a DC reduction motor is assembled by a reducer and a DC motor. The planetary gear motor is a reduction device assembled from a planetary gear box integrated drive motor, and a worm gear reducer is a reduction transmission device assembled from a worm gear box integrated motor motor. Application scenarios of different types of reduction motors It's not the same. Geared motors are usually produced by professional reducer and gearbox manufacturers. After they are integrated and assembled, they are supplied as a complete set with the motor, which can avoid loss and improve product quality.
DC motor is a rotating device that converts DC electrical energy into mechanical energy. The stator of the motor provides the magnetic field, the DC power supply provides current to the windings of the rotor, and the commutator keeps the direction of the torque generated by the rotor current and the magnetic field unchanged. According to whether or not it is equipped with a commonly used brush-commutator, DC motors can be divided into two categories, including brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors. DC motors without integrated assembly reducer (gearbox) do not have the function of reduction transmission.
The DC reduction motor, namely the gear reduction motor, is based on the ordinary DC motor, plus a matching gear reduction box. The function of the gear reducer is to provide a lower speed and a larger torque. At the same time, different reduction ratios of the gearbox can provide different speeds and torques. This greatly improves the utilization rate of DC motors in the automation industry. Geared motor refers to the integrated body of reducer and motor (motor). Such an integrated body can also be commonly referred to as a gear motor or a gear motor. Usually integrated and assembled by a professional reducer manufacturer, it is supplied as a complete set. Geared motors are widely used in the steel industry, machinery industry, etc. The advantage of using a geared motor is to simplify the design and save space.

The DC reduction motor, that is, the gear DC reduction motor, is based on the usual DC reduction motor, plus a matching gear reduction box. The function of the gear reducer is to provide a lower speed and a larger torque. Gearboxes with different reduction ratios can provide different speeds and torques. This has greatly increased the use rate of DC geared motors in the automation industry.
1. According to the type of operating power supply: it can be divided into DC gear motor and communication motor.
DC motors can be distinguished according to their layout and operating principles: brushless DC motors and brushed DC motors.
Brushed DC motors can be distinguished: permanent magnet DC motors and electromagnetic DC motors.
Electromagnetic DC motors are distinguished: series-excited DC motors, shunt-excited DC motors, separately-excited DC motors and compound-excited DC motors.
Permanent magnet DC motors are distinguished: rare earth permanent magnet DC reduction motors, ferrite permanent magnet DC motors and Alnico permanent magnet DC motors.
2. The communication motor can also be divided into: single-phase motor and three-phase motor.
According to the layout and operating principles: it can be divided into DC motors, asynchronous motors, and synchronous motors.
Synchronous motors can be distinguished: permanent magnet synchronous motors, reluctance synchronous motors and hysteresis synchronous motors.
Asynchronous motors can be distinguished: induction motors and commutator motors.
Induction motors can be distinguished: three-phase asynchronous motors, single-phase asynchronous motors and shaded-pole asynchronous motors.
Communication commutator motors can be distinguished: single-phase series motors, AC and DC motors and repulsion motors.
3. According to starting and working methods: capacitor-starting single-phase asynchronous motor, capacitor-operating single-phase asynchronous motor, capacitor-starting single-phase asynchronous motor and split-phase single-phase asynchronous motor.
4. Distinguish by purpose: drive motor and control motor.
Differentiation of driving motors: motors for electric things (including drilling, polishing, polishing, slotting, cutting, reaming, etc.), home appliances (including washing machines, electric fans, refrigerators, air conditioners, tape recorders, video recorders, and DVDs) Motors for machines, vacuum cleaners, cameras, hair dryers, electric shavers, etc.) and motors for other general small machinery equipment (including various small machine tools, small machinery, medical equipment, electronic instruments, etc.).
Control motors are divided into stepping motors and servo motors.
5. Distinguish according to the layout of the rotor: cage induction motors (called squirrel cage asynchronous motors in the old specification) and wound rotor induction motors (called winding asynchronous motors in the old specification).
6. Distinguish by working speed: high-speed motor, low-speed motor, constant-speed motor, speed-regulating motor. Low-speed motors are divided into geared DC reduction motors, electromagnetic reduction motors, torque motors and claw-pole synchronous motors.
In addition to stepped constant speed motors, stepless constant speed motors, stepped variable speed motors and stepless variable speed motors, speed regulating motors can also be divided into electromagnetic speed regulating motors, DC speed regulating motors, PWM variable frequency speed regulating motors and Switched reluctance speed motor.
The rotor speed of an asynchronous motor is always slightly lower than the synchronous speed of the rotating magnetic field.
The rotor speed of the synchronous motor has nothing to do with the size of the load and always maintains a synchronous speed.
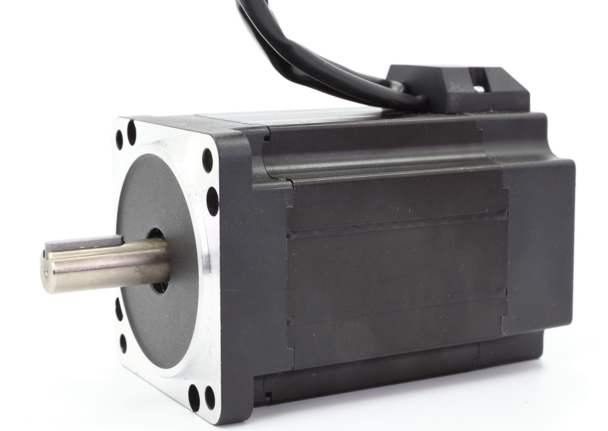

Ordinary DC motors generally have a high speed and a small torque, which is suitable for occasions with small torque requirements.
The DC reduction motor, that is, the gear reduction motor, is based on the ordinary DC motor, plus a matching gear reduction box. The function of the gear reduction box is to provide a lower speed and a larger torque. At the same time, the gear box has different speed reductions. It can provide different speeds and torques. This greatly improves the utilization rate of DC motors in the automation industry.
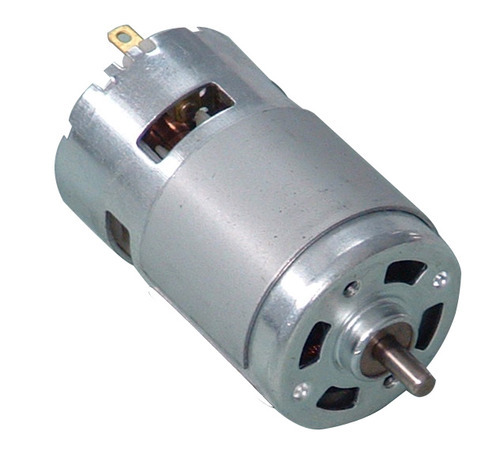
A DC motor is a motor that converts DC electrical energy into mechanical energy. Because of its good speed regulation performance, it is widely used in electric drive. According to the excitation mode, DC motors are divided into three types: permanent magnet, separate excitation and self-excitation. Among them, self-excitation is divided into three types: parallel excitation, series excitation and compound excitation.
When the DC power supply supplies power to the armature winding through the brush, the N-pole lower conductor on the armature surface can flow current in the same direction. According to the left-hand rule, the conductor will receive a counterclockwise torque; the S-pole lower part of the armature surface The conductor also flows in the same direction, and according to the left-hand rule, the conductor will also be subjected to a counterclockwise moment. In this way, the entire armature winding, that is, the rotor, will rotate counterclockwise, and the input DC electrical energy will be converted into mechanical energy output on the rotor shaft. It is composed of stator and rotor. Stator: base, main magnetic pole, commutating pole, brush device, etc.; Rotor (armature): armature core, armature winding, commutator, shaft and fan, etc.
structure
Basic structure
It is divided into two parts: stator and rotor. Note: Do not confuse the commutator with the commutator.
The stator includes: main magnetic pole, frame, commutating pole, brush device, etc.
The rotor includes: armature core, armature winding, commutator, shaft, fan, etc.
Rotor composition
The rotor part of the DC motor is composed of an armature core, an armature, a commutator and other devices. The components in the structure are described in detail below.
1. Armature core part: its function is to embed the discharge armature winding and reverse the magnetic flux, in order to reduce the eddy current loss and hysteresis loss in the armature core when the motor is working.
2. Armature part: the function is to generate electromagnetic torque and induced electromotive force, and carry out energy conversion. The armature winding has many coils or glass fiber coated flat steel copper wire or strength enameled wire.
3. The commutator is also called the commutator. In a DC motor, its function is to convert the current of the DC power supply on the brush into the communication current in the armature winding, so that the tendency of electromagnetic torque is stable. In the generator, it transforms the electromotive force of the armature winding into the DC electromotive force output on the brush end.

The commutator is insulated with mica between the cylinders composed of many pieces, and the two ends of each coil of the armature winding are separately connected to two commutating pieces. The function of the commutator in the DC generator is to convert the alternating electric heat in the armature windings into the DC electromotive force between the brushes. There is current passing through the load, and the DC generator outputs electric power to the load. At the same time, the armature coil is also There must be current passing through. It interacts with the magnetic field to generate electromagnetic torque, and its tendency is opposite to that of a generator. The original idea only needs to suppress this magnetic field torque to change the armature. Therefore, when the generator outputs electrical power to the load, it outputs mechanical power from the original idea, completing the function of the DC generator to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Gear reduction motor refers to a combination of a gear reduction box and a motor (motor). This kind of composition can also be called a gearbox motor or a geared motor, and is usually supplied as a complete set after being integrated and assembled by a professional gear reducer manufacturer.
Geared motors are widely used and are indispensable power transmission equipment for automated machinery and equipment, especially in packaging machinery, printing machinery, corrugated machinery, color box machinery, conveying machinery, food machinery, three-dimensional parking lot equipment, automatic storage, and three-dimensional warehouses. , Chemical, textile, dyeing and finishing equipment. Miniature geared motors are also widely used in electronic locks, optical equipment, precision instruments, financial equipment and other fields.
working principle
Gear reducer motors generally use electric motors, internal combustion engines or other high-speed running power to drive the large gears to a certain deceleration through the pinion on the input shaft of the gear reducer (or reduction box), and then adopt a multi-stage structure to achieve a certain deceleration. Greatly reduce the speed to increase the output torque of the geared motor. Its core function of "increasing and decelerating" is to use all levels of gear transmission to achieve the purpose of speed reduction, and the reducer is composed of various levels of gear pairs.
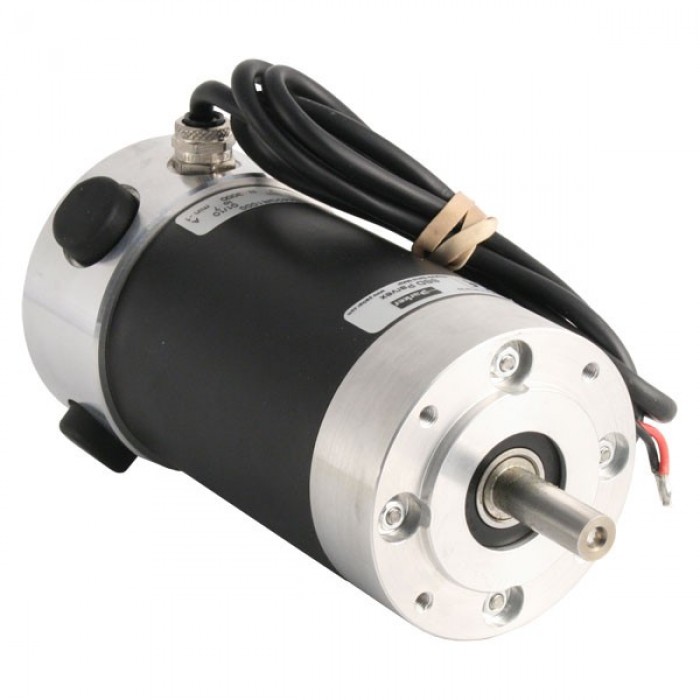

1. The geared motor is manufactured in accordance with international technical requirements and has a high technological content.
2. Compact structure, reliable and durable, high overload capacity and high power.
3. Low energy consumption, superior performance, and the reducer efficiency is as high as 95%.
4. Low vibration, low noise, high energy saving, high-quality section steel material, rigid cast iron box body, high-end gear reducer motor adopts special aluminum alloy die-cast box body, and the surface of the gear is high-frequency heat treated.
5. After precision processing to ensure positioning accuracy, the gear reducer motor of the gear transmission assembly of the reducer can be equipped with various mainstream motors in the market, forming a new product feature of electromechanical integration and modular structure, which fully guarantees the quality characteristics of the product.
6. The product adopts serialized and modular design ideas, and has a wide range of adaptability. It can be combined with various motors, installation positions and structural schemes, and the gear reducer can choose any speed and various structural forms according to actual needs.
Types
Small gear reducer motor
Medium gear reducer motor
Large gear reducer motor
1. Speed ratio, that is, determine the operating speed of the machine, and then calculate the speed ratio of the geared motor based on the speed of the machine. Available formulas (speed ratio=input speed/output or motor speed/mechanical demand speed).
2. The torque can be selected according to the actual size of the machine. The torque of the gear reduction motor can be selected according to the torque table and selected according to the actual needs.