Motor refers to an electromagnetic device that realizes the conversion or transmission of electric energy according to the law of electromagnetic induction.
The motor is represented by the letter M in the circuit (the old standard is D). Its main function is to generate driving torque. As the power source for electrical appliances or various machinery, the generator is represented by the letter G in the circuit. Its main function is The role is to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Division:
1. Divided according to the type of power supply: it can be divided into DC motors and AC motors.
1) DC motors can be divided according to structure and working principle: brushless DC motors and brushed DC motors.
Brushed DC motors can be divided into: permanent magnet DC motors and electromagnetic DC motors.
Electromagnetic DC motors are divided into: series-excited DC motors, shunt-excited DC motors, separately-excited DC motors and compound-excited DC motors.
Permanent magnet DC motors are divided into: rare earth permanent magnet DC motors, ferrite permanent magnet DC motors and alnico permanent magnet DC motors.
2) AC motors can also be divided into: single-phase motors and three-phase motors.
2. According to the structure and working principle, it can be divided into DC motors, asynchronous motors and synchronous motors.
1) Synchronous motors can be divided into: permanent magnet synchronous motors, reluctance synchronous motors and hysteresis synchronous motors.
2) Asynchronous motors can be divided into induction motors and AC commutator motors.
Induction motors can be divided into three-phase asynchronous motors, single-phase asynchronous motors and shaded-pole asynchronous motors.
AC commutator motors can be divided into: single-phase series motors, AC and DC motors and repulsion motors.
Each motor has different functions, so the price of each motor will vary.


3. According to the starting and operating modes, it can be divided into: capacitor-starting single-phase asynchronous motor, capacitor-operating single-phase asynchronous motor, capacitor-starting single-phase asynchronous motor and split-phase single-phase asynchronous motor.
4. According to the purpose, it can be divided into: drive motor and control motor.
1) Drive motors can be divided into: motors for electric tools (including tools for drilling, polishing, polishing, grooving, cutting, reaming, etc.), home appliances (including washing machines, electric fans, refrigerators, air conditioners, tape recorders, and video recorders) , DVD players, vacuum cleaners, cameras, hair dryers, electric shavers, etc.) and other general small mechanical equipment (including various small machine tools, small machinery, medical equipment, electronic equipment, etc.) motors.
2) The control motors are divided into stepping motors and servo motors.
5. According to the structure of the rotor can be divided: cage induction motor (old standard called squirrel cage asynchronous motor) and wound rotor induction motor (old standard called wound asynchronous motor).
6. According to the operating speed, it can be divided into: high-speed motor, low-speed motor, constant-speed motor, and speed-regulating motor. Low-speed motors are divided into gear reduction motors, electromagnetic reduction motors, torque motors and claw-pole synchronous motors.
Speed regulating motors can be divided into stepped constant speed motors, stepless constant speed motors, stepped variable speed motors and stepless variable speed motors, but can also be divided into electromagnetic speed regulating motors, DC speed regulating motors, PWM variable frequency speed regulating motors and Switched reluctance speed motor.
The rotor speed of an asynchronous motor is always slightly lower than the synchronous speed of the rotating magnetic field.
The rotor speed of the synchronous motor has nothing to do with the size of the load and always maintains the synchronous speed.
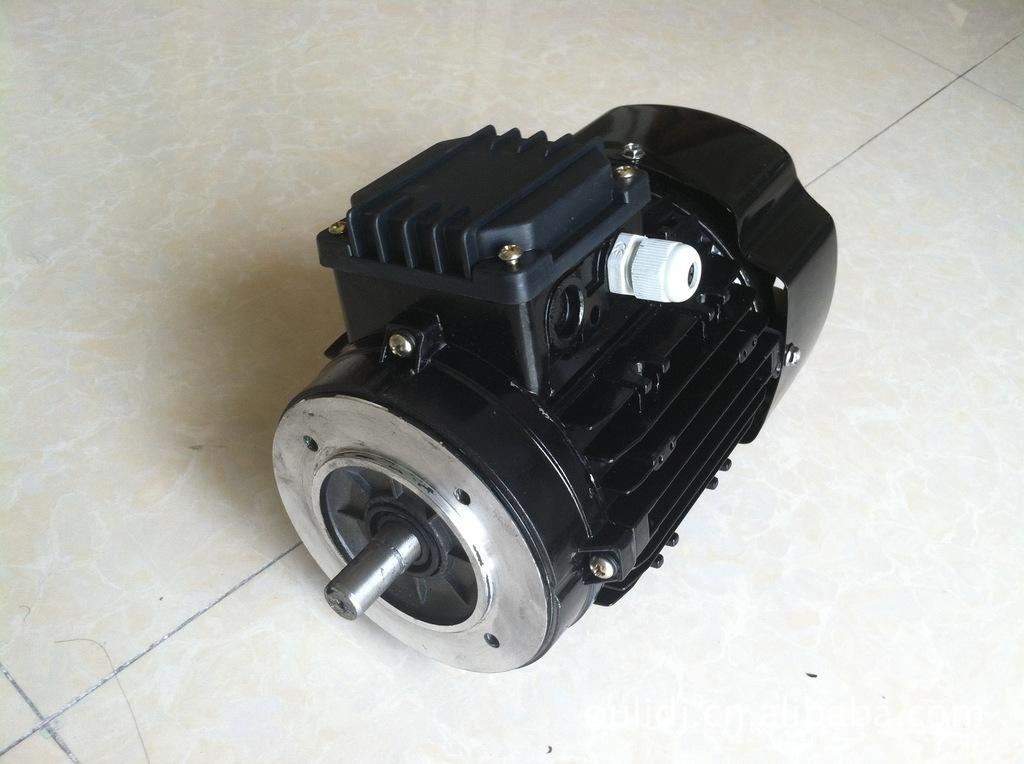




First, the direct current:
The working principle of the DC generator is to convert the alternating electromotive force induced in the armature coil into a DC electromotive force when it is drawn from the brush end by the commutator and the commutation action of the brush.
The direction of the induced electromotive force is determined according to the right-hand rule (the magnetic line of induction points to the palm of the hand, the thumb points to the direction of movement of the conductor, and the other four fingers point to the direction of the induced electromotive force in the conductor).
working principle:
The direction of the conductor's force is determined by the left-hand rule. This pair of electromagnetic forces forms a moment that acts on the armature. This moment is called electromagnetic torque in a rotating electric machine. The direction of the torque is counterclockwise, in an attempt to make the armature rotate counterclockwise. If this electromagnetic torque can overcome the resistance torque on the armature (such as resistance torque caused by friction and other load torques), the armature can rotate in a counterclockwise direction.
A DC motor is a motor that runs on a DC working voltage and is widely used in tape recorders, video recorders, DVD players, electric shavers, hair dryers, electronic watches, toys, etc.
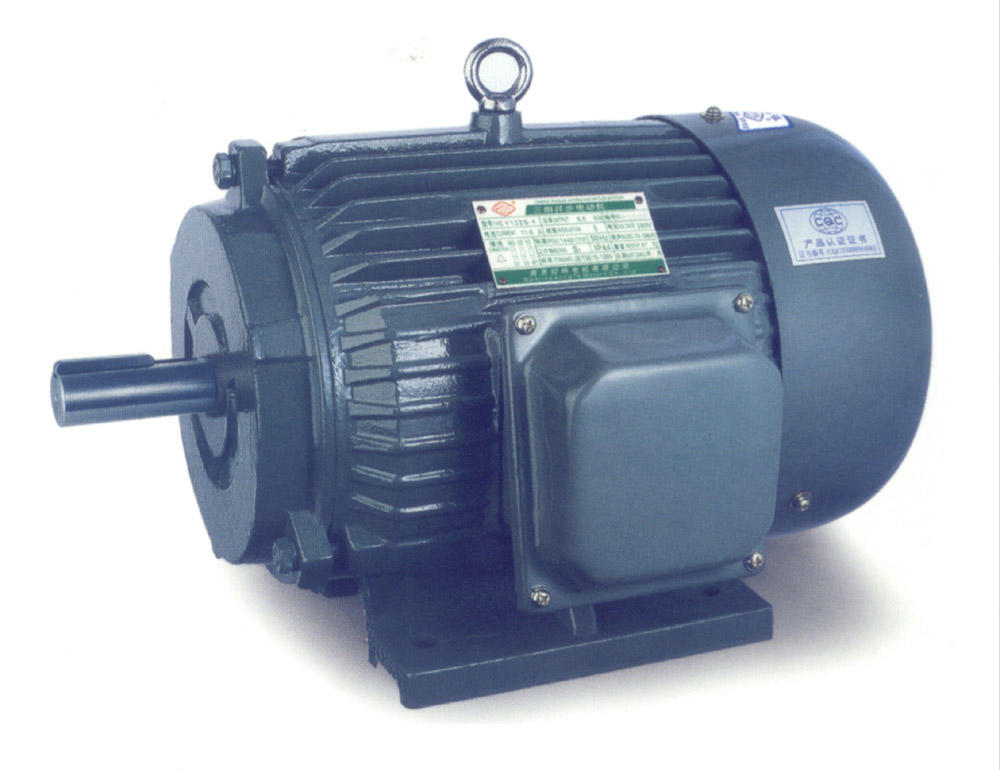

Second, the electromagnetic type:
Electromagnetic DC motors are composed of stator poles, rotor (armature), commutator (commonly known as commutator), brushes, casing, bearings, etc.
The stator magnetic poles (main magnetic poles) of an electromagnetic DC motor are composed of an iron core and an excitation winding. According to the different excitation methods (called excitation in the old standard), it can be divided into series-excited DC motors, shunt-excited DC motors, separately-excited DC motors and compound-excited DC motors. Due to the different excitation methods, the law of the stator magnetic pole flux (generated by the excitation coil of the stator pole is energized) is also different.
The field winding and the rotor winding of the series-excited DC motor are connected in series through the brush and the commutator. The field current is proportional to the armature current. The magnetic flux of the stator increases with the increase of the field current. The torque is similar to the electric current. The armature current is proportional to the square of the current, and the speed drops rapidly as the torque or current increases. The starting torque can reach more than 5 times the rated torque, and the short-term overload torque can reach more than 4 times the rated torque. The speed change rate is large, and the no-load speed is very high (generally not allowed to run under no-load ). Speed regulation can be achieved by connecting an external resistor in series (or in parallel) with the series winding, or switching the series winding in parallel.
The excitation winding of the shunt-excited DC motor is connected in parallel with the rotor winding, the excitation current is relatively constant, the starting torque is proportional to the armature current, and the starting current is about 2.5 times the rated current. The speed decreases slightly with the increase of current and torque, and the short-term overload torque is 1.5 times of the rated torque. The rate of speed change is small, ranging from 5% to 15%. The speed can be adjusted by weakening the constant power of the magnetic field.
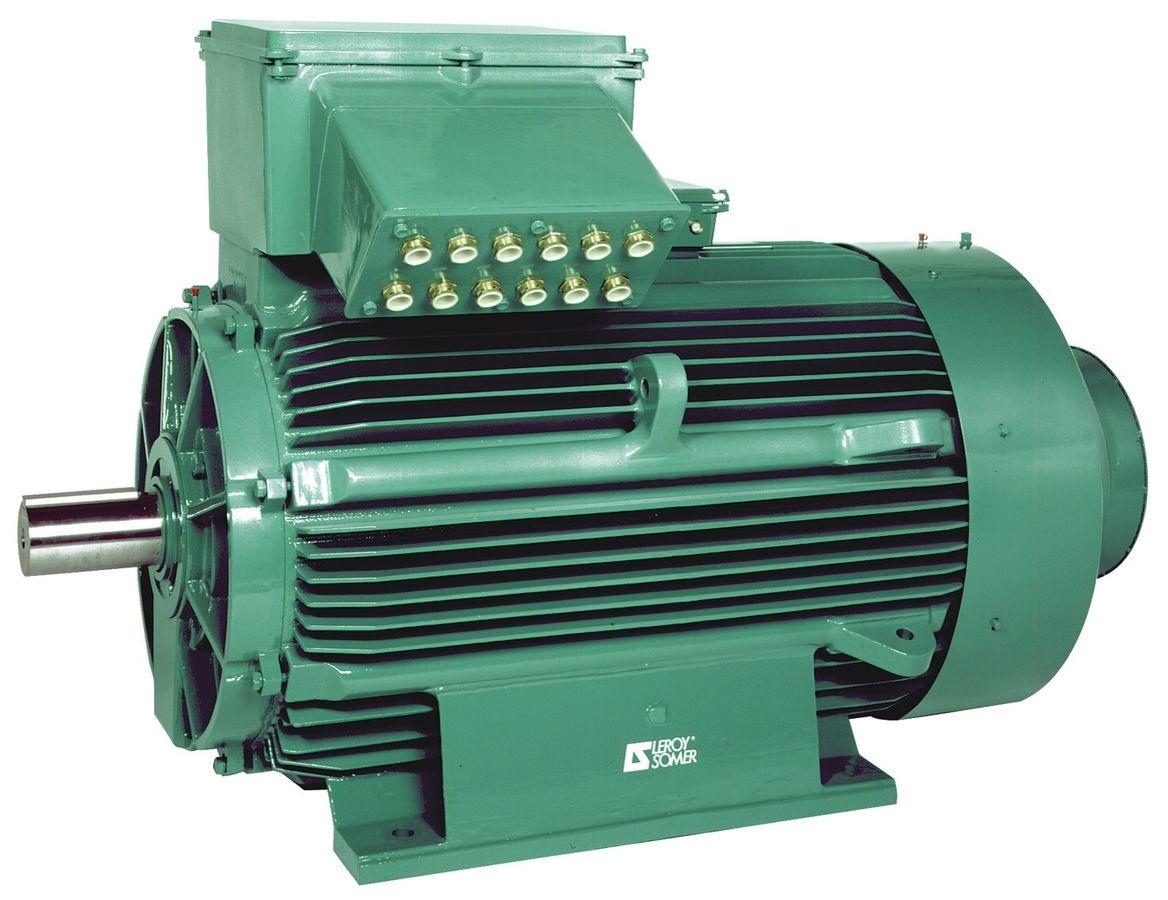

The excitation winding of the separately excited DC motor is connected to an independent excitation power supply, and its excitation current is relatively constant, and the starting torque is proportional to the armature current. The speed change is also 5%~15%. The speed can be increased by weakening the magnetic field and constant power or by reducing the voltage of the rotor winding to reduce the speed.
In addition to the shunt winding on the stator magnetic poles of the compound-excited DC motor, a series winding (with fewer turns) connected in series with the rotor winding is also installed. The direction of the magnetic flux generated by the series winding is the same as that of the main winding. The starting torque is about 4 times the rated torque, and the short-term overload torque is about 3.5 times the rated torque. The speed change rate is 25%~30% (related to series winding). The speed can be adjusted by weakening the magnetic field strength.
The commutator segments of the commutator are made of alloy materials such as silver-copper, cadmium-copper, and molded with high-strength plastic. The brushes are in sliding contact with the commutator to provide armature current for the rotor winding. The brushes of electromagnetic DC motors generally use metal graphite brushes or electrochemical graphite brushes. The iron core of the rotor is made of laminated silicon steel sheets, generally 12 slots, with 12 sets of armature windings embedded, and each winding is connected in series, and then connected to 12 commutating plates.
Third, the DC motor:
The excitation method of the DC motor refers to the problem of how to supply power to the excitation winding and generate the magnetomotive force to establish the main magnetic field. According to different excitation methods, DC motors can be divided into the following types.
Ta Li
The field winding has no connection relationship with the armature winding, and the DC motor powered by other DC power supply to the field winding is called a separately excited DC motor. Permanent magnet DC motors can also be regarded as separately excited DC motors.
Encourage
The excitation winding of the shunt-excited DC motor is connected in parallel with the armature winding. As a shunt-excited generator, the terminal voltage from the motor itself supplies power to the field winding; as a shunt-excited motor, the field winding and armature share the same power source, which is the same as a separately-excited DC motor in terms of performance.
Cross excitation
After the field winding of the series-excited DC motor is connected in series with the armature winding, it is connected to the DC power supply. The excitation current of this DC motor is the armature current.

Compound excitation
Compound-excited DC motors have two excitation windings: shunt excitation and series excitation. If the magnetomotive force generated by the series winding is in the same direction as the magnetomotive force generated by the shunt winding, it is called product compound excitation. If the two magnetomotive forces have opposite directions, it is called differential compound excitation.
DC motors with different excitation methods have different characteristics. In general, the main excitation modes of DC motors are shunt excitation, series excitation and compound excitation, and the main excitation modes of DC generators are separate excitation, shunt excitation and compound excitation.
Fourth, the permanent magnet type:
Permanent magnet DC motors are also composed of stator poles, rotors, brushes, housings, etc. The stator poles use permanent magnets (permanent magnets), including ferrite, alnico, neodymium iron boron and other materials. According to its structure, it can be divided into cylinder type and tile type. Most of the electricity used in VCRs are cylindrical magnets, while the motors used in electric tools and automotive electrical appliances mostly use special block magnets.
The rotor is generally made of laminated silicon steel sheets, which has fewer slots than the electromagnetic DC motor rotor. The low-power motors used in VCRs are mostly 3 slots, and the higher-end ones are 5 slots or 7 slots. The enameled wire is wound between the two slots of the rotor core (three slots means three windings), and its joints are respectively welded to the metal sheet of the commutator. The brush is a conductive part that connects the power supply and the rotor winding. It has both conductive and wear-resistant properties. The brushes of permanent magnet motors use single-sex metal sheets, metal graphite brushes, and electrochemical graphite brushes.
The permanent magnet DC motor used in the VCR adopts electronic speed stabilization circuit or centrifugal speed stabilization device.

Common sense of motor protection:
1. Motors are easier to burn out than in the past: Due to the continuous development of insulation technology, the design of motors requires both increased output and reduced size, so that the heat capacity of the new motor is getting smaller and the overload capacity is getting weaker; Due to the increase in the degree of production automation, the motors are required to run frequently in various ways such as frequent starting, braking, forward and reverse rotation, and variable load, which puts forward higher requirements for motor protection devices. In addition, the motor has a wider range of applications, often working in extremely harsh environments, such as humidity, high temperature, dust, and corrosion. All of these make the motor more prone to damage, especially the highest frequency of faults such as overload, short circuit, phase loss, and bore sweeping.
2. The protection effect of the traditional protection device is not ideal: the traditional motor protection device is mainly thermal relay, but the thermal relay has low sensitivity, large error, poor stability and unreliable protection. The fact is also true. Although many devices are equipped with thermal relays, the phenomenon of damage to the motor that affects normal production is still widespread.