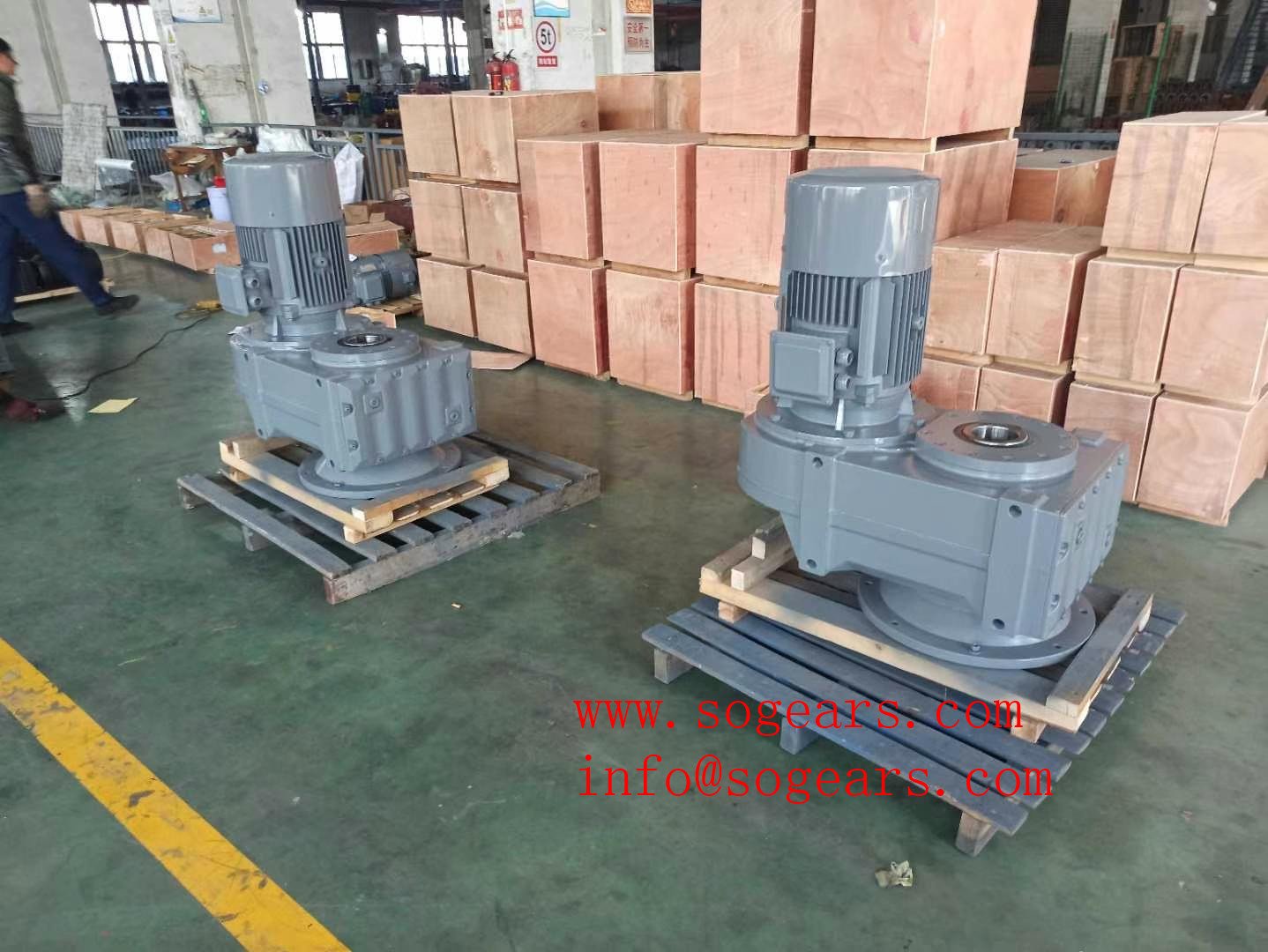
Analysis of three phase inverter connection.
A three phase inverter connection with a neutral connection i.e., three phase four wire inverter is proposed. The UPS system is fed by three phase four wire inverter and the load neutral point voltage is low to meet the requirement of the system. The four leg inverters effectively provide the neutral connection in three phase four wire system. They are used in many applications to handle the neutral current caused by the unbalanced and non-linear load. The unbalanced load becomes non-linear where the neutral of the loads are accessible. The four leg inverter produces the three output voltages independently with one additional leg. The main feature of a three phase inverter with an additional neutral leg is its ability to deal with load unbalance in a system. The goal of the three phase four leg inverter is to maintain the desired sinusoidal output voltage waveform for all loading conditions and transients. The neutral connection is present to handle the ground current due to unbalanced loads. The feasibility of the proposed modulation technique is verified by Matlab/Simulink.
A novel approach to adapt a conventional direct power control (DPC) for high-power applications, where a third-order LCL filter is frequently required. The LCL filter can cause a strong resonance and requires additional effort for system control. The application of a DPC for the control of a three phase inverter connection voltage source inverter that is connected to the grid through an filter has not yet been considered. Analysis of three phase inverter connection.The addition of an active damping strategy, together with a harmonic rejection control loop, to the conventional DPC is proposed and analyzed in this paper. The steady-state, as well as the dynamic performance of the proposed system, is verified with simulation results and experimental measurements.
Direct current-space-vector control of an active power filter (APF) based on a tthree phase inverter connection. The proposed method indirectly generates the compensation current reference by using an equivalent conductance of the fundamental component using APF's dc-link voltage control. The proposed control can selectively choose harmonic current components by real-time fast Fourier transform to generate the compensation current. The compensation current is represented in a rotating coordinate system with chosen switching states from a switching table implemented in a field-programmable gate array. In addition, a three-phase four-wire APF based on a three-level neutral-point-clamped inverter is also presented. The proposed APF eliminates harmonics in all three phases as well as the neutral current. A three-phase three-wire NPC inverter system can be used as a three-phase four-wire system since the split dc capacitors provide a neutral connection.

The increasing presence of single-phase distributed generators and unbalanced loads in the electric power system may lead to unbalance of the three phase voltages, resulting in increased losses and heating. The distribution network operators (DNOs) are increasingly being challenged to maintain the required power quality. To reduce voltage unbalance DNOs are seeking to connect larger DG units to the three phases instead of a single-phase connection. The three phase inverter connection can be realised by three phase inverter connection or by a three-phase inverter. Each inverter topology can be implemented with different control strategies. The control can be equiped with active power filtering functions which can improve the power quality. In this paper, the effect of connecting DG units by means of a three phase inverter connection of a single-phase connection on voltage unbalance is studied.
Series connection of power cells in asymmetrical cascaded configurations helps to cancel redundant output levels and maximise the number of different levels generated by the inverter. A new configuration of three phase inverter connection asymmetrical cascaded voltage source inverter is presented. This structure consists of series-connected sub-multilevel inverters blocks. The number of utilised switches, insulated gate driver circuits, voltage standing on switches, installation area and cost are considerably reduced. Cascaded-cell DC voltages in each inverter leg form an arithmetic sequence with common difference of E. With the selected inverter DC sources, high-frequency pulse-width modulation (PWM) control methods can be effectively applied without loss of modularity. Low-frequency and sinusoidal PWM techniques were successfully applied. Hence, high flexibility in the modulation of the proposed inverter is demonstrated.
A small and highly vibration-proof inverter capable of detecting a phase current without requiring the development of complicated control software and without causing any current distortion is provided. Shunt resistors serving as a kind of current detector are provided, respectively, between lower arm switching elements in only two phases—and the minus side of a DC power supply.Analysis of three phase inverter connection. An identical ON period is reduced from the ON periods of upper arm switching elements in the carrier cycle entirely for three phases. Consequently, phase current is detected for the two phases provided with the shunt resistors . The inverter can detect the phase current without complicating the control software and without causing any current distortion, by controlling inverter circuit with control software incorporated in control circuit through connection lines .
Power converters in grid connection applications commonly employ Sinusoidal Pulse-Width Modulation (SPWM) technique. Passive filters are employed in order to attenuate the generated switching current ripples and reduces resonances between the grid and the inverter. The first-order, the second-order, and the three phase inverter connection are typical filters for grid connected Voltage Source Inverters. Practically, due to the system size, weight, and cost requirements, the LCL filter is the most commonly used among others for the integration of the three phase VSI into the grid. However, the control system stability is affected by the underdamping characteristic of the LCL filter therefore, it introduces to challenges to the control problem. Numerous control strategies such as repetitive, predictive, multiloop control, and hysteresis regulation have been proposed in order to improve the stability of the grid-connected VSIs.

Three phase double mode inverter system was researched in this paper, whose input was battery bank system with PV generation. This system can be operated in stand-alone mode by connecting to local load and also in grid-connected mode by paralleling with grid. When in stand-alone mode, system worked as voltage source, while when in grid-connected mode, the output current of inverter was controlled following with grid. A transition algorithm to restrain current inrush and fast detection of switch and grid status make sure the seamless transition between grid-connected and stand-alone. This inverter system has advantage of simple structure and easy to implement, so that it was appropriate for micro-grid.
The proposed work is to design a power electronic converter to reduce the power quality issues. Due to the increased usage of power electronic converters for processing the power, the power quality issues become the hot research topic in the recent past. As the power level increases, the voltage level is increased accordingly to obtain satisfactory efficiency. During the last decades, the voltage rating of fast switching high voltage semiconductors such as the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) has increased. Still, there is a need for series connection of switching devices. In this area of applications, the multilevel power converter has shown growing popularity. The fundamental advantages of the multilevel converter topologies are low distorted output waveforms and limited voltage stress on the switching devices and hence the reduced electromagnetic interferences on the output waveforms. The main disadvantages are higher complexity and more difficult control but it can be overcome by using modern digital controllers.
It has the same construction as the conventional three phase inverter connection inverter that is interconnected to the single-phase three-wire distribution system. Though the proposed circuit has no output transformer, it can be equivalently performed as the single-phase double cascade inverter by diverting the pole transformer in the utility system. By controlling the appropriate scheme, the output currents can be obtained as the five-level waveforms and their distortions can be decreased sufficiently. It is applied to the interactive electric energy storage system with batteries and the basic discharging characteristics are discussed experimentally.
With the increase in the use of renewable sources, the study of control schemes for better control of distributed generation systems and grid connection has become very vital to achieve better stability of the system. Analysis of three phase inverter connection.This thesis provides a study of the control scheme for interconnection between a DC source and an AC grid. A possible control scheme is studied and simulated in Simulink. The system behavior is analyzed by subjecting it to different changes in parameters and grid conditions. The implementation of the scheme is done by using dSpace and Simulink model. Only Low Voltage implementation is performed and tested in this thesis.
The use of three-phase voltage inverters (DC to AC converters) is frequently met in the electric power system, such as in the connection of photovoltaics with the rest of the grid. The paper proposes a nonlinear feedback control method for three phase inverter connection, which is based on differential flatness theory and a new nonlinear filtering method under the name Derivative-free nonlinear Kalman Filter. First, it is shown that the inverter's dynamic model is a differentially flat one. This means that all its state variables and the control inputs can be written as functions of a single algebraic variable which is the flat output. By exploiting differential flatness properties it is shown that the inverter's model can be transformed to the linear canonical (Brunovsky's) form. For the latter description the design of a state feedback controller becomes possible, e.g. using pole placement methods. Moreover, to estimate the non-measurable state variables of the linearized equivalent of the inverter, the Derivative-free nonlinear Kalman Filter is used.

The mathematical model based on the Parks theory allows the analysis of the whole spectrum (electric car ; frequency inverter) to drive the electric trolley bus made on ASTRA Bus Arad . To remove higher order harmonics, the PWM waveform of supply voltage is used, set in the general case. Operating characteristics of electric motor drive are set to sub-nominal frequency and for different angles of the control switching elements in the construction of the inverter. Tensions in the stator of the equivalent machine are determined by three components: the fundamental component; the second component corresponding to the higher order harmonics, which rotate in direct connection; and the appropriate third component of higher order harmonics, which are rotated in reverse. The mathematical model developed will help to determine the harmonics which have a negative influence on the performance.
The thesis is concerned with the use of flywheel energy storage system in utility load levelling application. The work presented consists of two parts, first, an evaluation of utility load levelling schemes with FESS as the energy storage medium, and second, the development of power electronic interface of FESS to the utility. The thesis presents a study to evaluate FESS load levelling schemes in a UK electricity supply and distribution company. It identifies and quantifies the costs and benefits of the schemes, and carries out a financial appraisal based on Net Present Value and Internal Rate of Return methods. The results indicate that the DSM schemes utilising FESS can be financially viable for a UK electricity supply and distribution business in a mass-produced FESS scenario, and provide FESS manufacturers and developers with cost goals for such applications. The conclusions drawn provide the motivation for further technical research undertaken within the programme of work.
Compared with traditional controllers such as PI based on classic control theory, the article applies passive control theory to the design of three-phase LCL grid-connected inverter controllers. The mathematical model of the system based on Euler-Lagrange is established, and the damping method of the trap is used to suppress the resonance spikes generated by the system, so that the system meets the requirements of grid connection. The simulation results verify the feasibility of the scheme.
As a commercial interface, three-phase voltage-source inverters (VSI) are commonly equipped for energy conversion to export DC power from most distributed generation (DG) to the AC utility. Not only do voltage-source converters take charge of converting the power to the loads but support the grid voltage at the point of common connection (PCC) as well, which is dependent on the condition of the grid-connected loads. This paper explores the border collision and its interacting mechanism among the VSI, resistive interacting loads and grids, which manifests as the alternating emergence of the inverting and rectifying operations, where the normal operation is terminated and a new one is assumed.Analysis of three phase inverter connection. Their mutual effect on the power quality under investigation will cause the circuital stability issue and further deteriorate the voltage regulation capability of VSI by dramatically raising the grid voltage harmonics. It is found in a design-oriented view that the border collision operation will be induced within the unsuitable parameter space with respect to transmission lines.
Nowadays the multilevel inverters are widely used in power electronic applications. The multilevel inverters are recommended for medium and high voltage applications. Multilevel inverters have become more popular due to reduced switching losses, low costs, low harmonic distortion and high voltage capability when compared to traditional PWM inverters. This paper deals with hybrid multilevel converter which is synthesize of neutral point clamped and cascaded multilevel inverter. The hybrid multilevel converter is proposed for medium voltage large power ratings. The proposed converter consisting of voltage source inverter connected with half bridge modules at each phase. With the proposed connection large portion of energy can be preceded by the VSI by connecting single multi pulse rectifier. The smaller power shares processed within the half bridge modules. The modulation scheme for hybrid multilevel inverter is naturally achieved by using logic circuit.

With the growing use of inverters in distributed generation, the problem of injected harmonics becomes critical. These harmonics require the connection of low pass filters between the inverter and the network. This paper presents a design method for the output LC filter in grid coupled applications in distributed generation systems. The design is according to the harmonics standards that determine the level of current harmonics injected into the grid network. Analytical expressions for the maximum inductor ripple current are derived. The filter capacitor design depends on the allowable level of switching components injected into the grid. Different passive filter damping techniques to suppress resonance affects are investigated and evaluated. Simulated results are included to verify the derived expressions.
A two-level four-leg inverter has been developed for the three-phase four-wire power quality compensators. When it is applied to medium and large capacity compensators, the voltage stress across each switch is so high that the corresponding dv/dt causes large electromagnetic interference. The multilevel voltage source inverter topologies are good substitutes, since they can reduce voltage stress and improves output harmonic contents. The existing three-level neutral point clamped (NPC) inverter in three-phase three-wire systems can be used in three-phase four-wire systems also, because the split dc capacitors provide a neutral connection. This paper presents a comparison study between the three-level four-leg NPC inverter and the three-level NPC inverter. A fast and generalized applicable three-dimensional space vector modulation (3DSVM) is proposed for controlling a three-level NPC inverter in a three-phase four-wire system. The zero-sequence component of each vector is considered in order to implement the neutral current compensation.
The bidirectional inverter can fulfill both grid connection and rectification modes with power factor correction. The proposed control includes two approaches, one line-cycle regulation approach (OLCRA) and one-sixth line-cycle regulation approach (OSLCRA), which take into account dc-bus capacitance and control dc-bus voltage to track a linear relationship between the dc-bus voltage and inverter inductor current. Since both of the approaches require the parameter of dc-bus capacitance, this paper first presents determination of dc-bus capacitor size and an online capacitance estimation method. With the OLCRA, the inverter tunes the dc-bus voltage every line cycle, which can reduce the frequency of operation-mode change and current distortion. The OSLCRA adjusts current command every one-sixth line cycle to adapt to abrupt dc-bus voltage variation.
The connection of distributed power sources with the utility grid generally needs an electronic power converter for processing the locally generated power and injecting current into the system. If the source provides a dc voltage, the converter must be able to produce a low-distortion high-power-factor ac current. The same aspects related with the voltage and current distortion produced by nonlinear loads can be considered for the injection of power into the grid. In the absence of a specific standard, this paper takes as a reference the limits for current harmonics given by international standards. The justification for this approach is that, from the resulting line voltage degradation, there is no difference between injected and absorbed currents. This paper presents a three-phase inverter using low-frequency commutation. An auxiliary circuit is added to the inverter topology to reduce the output voltage distortion, thus improving the current waveform.
In order to investigate the system performance for grid connection, a 50 kW photovoltaic power generation system including a three-phase DC/AC inverter is designed, made and constructed. This paper describes the system design and the performance of a 50 kW grid-tied PV plant, which consists of solar cells, DC/AC inverter, utility grid. Especially, the control scheme of a three phase current-controlled PWM inverter using d-q axis transformation is presented, and then the experimental results show that the proposed system has high efficiently stable behavior with a unity power factor in utility-interactive operation. Also the field test results show that the system utilization rate is about 13.4%.
Small-signal stability is an important concern in three-phase inverter-based ac power systems. The impedance-based approach based on the generalized Nyquist stability criterion (GNC) can analyze the stability related with the medium and high frequency modes of the systems. However, the GNC involves the right-half-plane (RHP) pole calculation of return-ratio transfer function matrices, which cannot be avoided for stability analysis of complicated ac power systems. Therefore, it necessitates the detailed internal control information of the inverters, which is not normally available for commercial inverters. To address this issue, this paper introduces the Component Connection Method (CCM) in the frequency domain for stability analysis in the synchronous d-q frame, by proposing a method of deriving the impedance matrix of the connection networks of inverter-based ac power systems.

Grid codes are being revised to include additional requirements for renewable energy, as the installed power increases. Therefore it is needed to develop control systems that are able to fulfil those new requirements, which usually include the ability to operate under unbalanced grid voltages without polluting the grid, among others. This paper presents a three-phase inverter for connection of photovoltaic generators to the grid, with a fuzzy maximum power point tracking and the ability to control reactive power. The main feature of the inverter is that the control system has been designed to deal with unbalanced voltage conditions.
A thyristor inverter having N parallel branches is controlled by an impulse supply source which normally excites the individual thyristors in each branch in cyclic succession. In the presence of an overload in a branch, the impulse source is switched to an override mode which simultaneously excites all of the inverter thyristors. A coil disposed in each of the inverter branches defines, with a reactive circuit including a storage capacitor connected across the branches, an oscillatory circuit. The inductance of the branch coils is chosen such that during the override mode, the oscillatory current is larger in magnitude than the overload current. The inverter thyristors are thus extinguished during the half-cycle of oscillation in which the polarity of the oscillation opposes that of the overload current. After such quench, the impulse source may either be disabled to prevent re-ignition of the thyristors, or switched back to its normal mode.
A DC to two-phase AC inverter that includes three one-leg switch mode inverters circuits or a three-phase bridge circuit and a controller/driver circuit. The controller/driver circuit includes a triangular waveform generator and two sinusoidal reference waveform generators out of phase with each other, the sinusoidal waveforms generated at the desired AC output frequency, and the triangular waveform generated at a higher frequency. The controller/driver circuit is configured to drive one leg of the bridge circuit with a 50% duty cycle at the triangular waveform frequency and the other two legs at the triangular waveform frequency with pulse width modulated signals, the pulse widths of each signal varying with a discrete one of the sinusoidal waveforms. Each phase of two-phase AC is provided by the inverter between the leg driven at the 50% duty cycle and a discrete one of the other legs.
Power converters in grid connection applications commonly employ Sinusoidal Pulse-Width Modulation technique. Passive filters are employed in order to attenuate the generated switching current ripples and reduces resonances between the grid and the inverter. The first-order, the second-order, and the third-order filters topologies are typical filters for grid connected Voltage Source Inverters . Practically, due to the system size, weight, and cost requirements, the LCL filter is the most commonly used among others for the integration of the three phase VSI into the grid. However, the control system stability is affected by the underdamping characteristic of the LCL filter therefore, it introduces to challenges to the control problem.Analysis of three phase inverter connection. Numerous control strategies such as repetitive, predictive, multiloop control, and hysteresis regulation have been proposed in order to improve the stability of the grid-connected VSIs.
Growing utilization of distributed generations in the power system may lead to protection problems. Therefore, in the conventional methods, DGs should be disconnected from the grid in the fault condition. In the case of high penetration of DGs, this strategy leads to voltage sag problem. In this paper, the inverter based DGs are properly controlled in the fault condition instead of disconnecting from the grid. This approach is called fault ride through strategy. The simulation results show that the fault current is kept in the desired range by using the proposed algorithm and the protection coordination before connection of DG remains intact even after the connection of DG. In addition, the voltage sag is improved due to DGs reactive power injection during the fault condition. Moreover, this method has not any additional cost because the proposed control strategy is carried out on the interfaced inverter and there is no need to use additional elements.